Imagine turning messy data into useful insights without handling a server. This AWS Glue tutorial for beginners shows how to use a managed ETL service. It makes data integration easier, perfect for cloud migrations and managing data lakes.
Today’s businesses face a sea of unstructured data. Old ETL tools are expensive and need constant upkeep. AWS Glue changes this with serverless architecture. It automates scaling, monitoring, and fixing errors. Plus, it connects well with services like Amazon Redshift, Athena, and S3.
This guide makes things simple. You’ll learn to make data catalogs, schedule jobs, and save money. We’ll use real examples to guide you, whether you’re getting data ready for machine learning or combining separate data.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Serverless architecture eliminates infrastructure management
- Built-in integration with AWS analytics services accelerates workflows
- Automated schema discovery reduces manual coding
- Pay-as-you-go pricing aligns with project scalability
- Centralized data catalog simplifies metadata tracking
What Is AWS Glue?
In today’s world, turning raw data into useful insights is key. AWS Glue makes this easier as a serverless data integration service. It automates the process of getting data ready for use. It’s like a cloud-based conductor, helping data move smoothly between places like S3 buckets and Redshift.
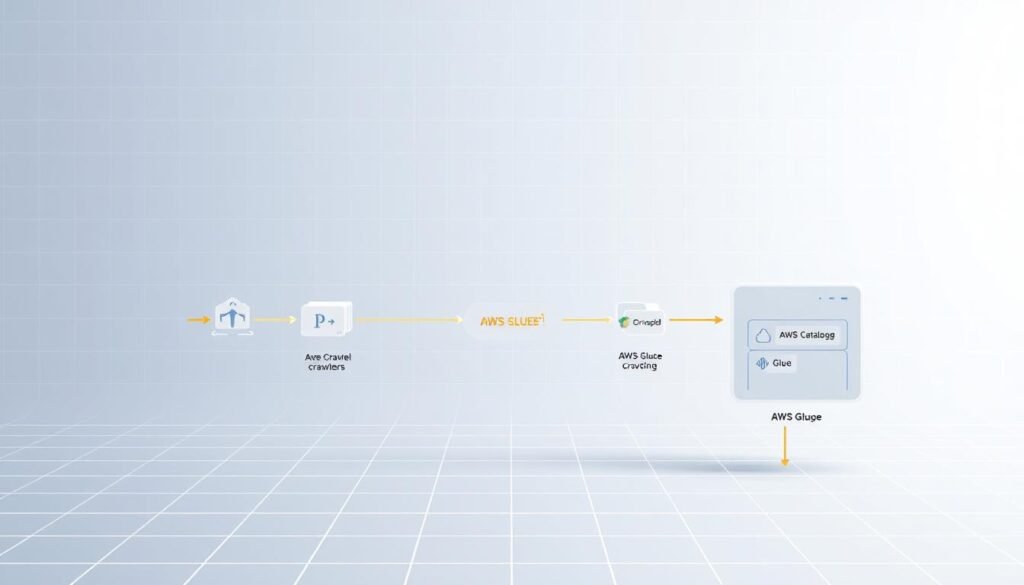
Serverless Data Integration Service Explained
AWS Glue takes care of the hard stuff, like managing servers. Unlike old ETL tools, it doesn’t need dedicated servers. You only pay for the time it uses to process data, so you save on costs.
Its main benefits are:
- It scales automatically for big datasets
- It has built-in error handling and job tracking
- It works well with AWS analytics services
Key Features for ETL Workflows
When you start with AWS Glue, you’ll find these important features:
- Data Catalog: A central place for all your data
- Smart Crawlers: Finds schema and format changes on its own
- Code Generation: Creates PySpark scripts for common tasks
How AWS Glue Fits in Modern Data Architecture
Modern systems need flexible data paths. AWS Glue connects different parts of your data flow. It links:
| Data Source | Processing | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| S3 Data Lakes | ETL Jobs | Redshift Warehouses |
| RDS Databases | Data Catalog | Athena Queries |
For example, moving SQL Server data to an S3 data lake is easier with Glue. It uses its managed infrastructure and schema detection. This lets analysts use the data in Athena quickly, not slowly.
AWS Glue Tutorial for Beginners: Core Concepts
Learning AWS Glue starts with three key ideas. These ideas are the base of data integration. They help turn raw data into useful insights. Let’s explore them with examples and analogies.

Understanding Data Catalog and Metadata
The AWS Glue Data Catalog is like a librarian for your data lake. It keeps track of your data sources, schema details, and version history. This is similar to how a library catalog works.
- Indexes data sources (S3 buckets, databases)
- Records schema details (column names, data types)
- Tracks data version history
When you start with this aws glue guide for beginners, you’ll see metadata management is automatic. For example, a retail company can track daily sales files. It automatically notices new CSV columns during holidays.
ETL vs ELT in AWS Glue
AWS Glue supports both ETL and ELT methods. Here’s a comparison:
| Approach | Process | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| ETL | Transform data before storage | Structured reporting |
| ELT | Store raw data first, transform later | Big data exploration |
As AWS architects often say:
ELT is preferred for cloud-native workflows because it’s flexible with unstructured data.
Managed Infrastructure Benefits
AWS Glue’s Data Processing Units (DPUs) handle scaling automatically. Unlike traditional systems, you don’t manage servers:
- The service allocates resources based on job complexity
- You only pay for DPU-hours consumed
- Maintenance and security updates happen automatically
This lets you focus on writing transformation logic, not hardware specs. When you learn AWS Glue step by step, you’ll see how this managed approach saves time. It reduces setup time from hours to minutes.
These core concepts lay the groundwork for the practical steps ahead. With metadata and infrastructure managed by AWS, you can focus on extracting value from your data.
Also Read: Amazon Redshift Tutorial for Beginners
Setting Up Your AWS Environment
Before you start with AWS Glue, you need a cloud environment set up. This guide covers three key steps: creating an account, setting up security, and configuring services. It’s all about getting started with aws glue for newbies.

Creating an AWS Account
First, go to the AWS Management Console:
- Click “Create a new AWS account”
- Enter your payment and contact details
- Choose the Free Tier to save money upfront
Make sure to verify your email right away. Also, turn on multi-factor authentication (MFA) for better security.
IAM Permissions for Glue Operations
Having the right permissions is key to avoid mistakes. Create an IAM role with:
- AWSGlueServiceRole policy
- AmazonS3FullAccess (temporary)
- CloudWatchLogs permissions
Pro Tip: Don’t use root credentials for everyday tasks. Companies should use Service Control Policies (SCPs) to limit access.
Configuring Required Services (S3, VPC)
Get these essential components ready:
| Service | Configuration | Glue Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| S3 | Create input/output buckets | Raw data storage |
| VPC | Enable DNS resolution | Secure connectivity |
Create VPC subnets across different availability zones for safety. Always check S3 bucket policies with the IAM policy simulator before linking to Glue.
Navigating the AWS Glue Console
Learning the AWS Glue interface is your first step to creating efficient data pipelines. We’ll explore the console’s layout. This will help you find tools quickly and monitor your workflows well.
Dashboard Overview
The home screen is like the control center for your ETL work. It shows:
- Active jobs and their status
- Recent crawler runs
- Data catalog stats
The quick access toolbar lets you quickly start a job or set up a database. The main panel updates live, showing how resources are used. This is key for this easy AWS Glue tutorial.
Key Navigation Elements
Three main menus control the console:
- ETL section: Manage jobs, triggers, and workflows
- Data Catalog: Handle databases, tables, and crawlers
- Monitoring: Access logs and performance metrics
Tip: Bookmark the Script Editor in Glue Studio. You’ll use it a lot for code changes.
Service Health Monitoring
The status panel uses colors like traffic lights:
- ● Green: Everything’s working fine
- ● Yellow: Some issues
- ● Red: Big problems
Check this before starting big tasks in your easy AWS Glue tutorial. Historical data helps spot busy times and bottlenecks.
Creating Your First Data Catalog
Starting your AWS Glue journey means organizing your data. The Data Catalog is like a central library for your data. It turns raw files into tables ready for queries. Let’s explore how to set this up with sample sales data.
Database Creation Steps
First, organize your data sources. AWS Glue databases are like folders for related tables. Here’s how to get started:
- Open the AWS Glue Console and go to Databases in the left menu
- Click Add database and name it (like
sales_analysis) - Add a description for your team
- Check your settings and create
Pro tip: Use the AWS CLI for quick tasks:aws glue create-database --database-input '{"Name":"sales_analysis"}'
Table Definition Process
Now, turn CSV files into tables you can query. AWS Glue guesses the schema, but you can tweak it:
- Go to Tables under your database
- Choose Add tables manually
- Point to your S3 bucket with sales data
- Check the schema and make any needed changes
| Raw CSV Column | Catalog Schema Type | Glue Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| order_date (text) | timestamp | Date format override |
| price (string) | double | Decimal separator handling |
| product_id (integer) | bigint | No changes needed |
This example from the AWS Glue tutorial shows how it makes messy data ready for analysis. Try out your catalog with Athena or Redshift Spectrum. Good metadata saves time later.
Working with AWS Glue Crawlers
AWS Glue Crawlers are like data detectives. They automatically scan storage systems to find formats and structures. For beginners, learning about crawlers is key to efficient data cataloging without manual tracking. Let’s see how to set up, schedule, and adjust these tools for tasks like updating Shopify product catalogs.
Crawler Configuration Essentials
Setting up your first crawler requires three important choices:
- Data Source Identification: Connect to S3 buckets, JDBC databases, or APIs like Shopify
- IAM Role Assignment: Give read access to source data and write access to the Data Catalog
- Output Configuration: Choose the target database and table prefix for organized cataloging
For incremental data loads, use the “Crawl new folders only” option. This stops full rescans when adding new Shopify product CSV files to existing S3 paths.
Schedule Management for Data Discovery
AWS Glue offers flexible scheduling to fit your data update patterns:
| Schedule Type | Use Case | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| On-demand | Irregular data updates | Low (pay per run) |
| Daily cron | Shopify nightly exports | Medium |
| Custom (CRON) | Real-time analytics pipelines | High |
Use a weekly schedule for moderate Shopify catalog changes. Use AWS cron syntax: cron(0 12 ? * SUN *) for Sunday noon scans.
Handling Schema Changes Automatically
AWS Glue makes schema evolution easy through:
- Versioned table definitions in the Data Catalog
- Optional schema change alerts via CloudWatch
- Backward-compatible type promotion (INT → BIGINT)
When Shopify adds new product attributes, your crawler will:
- Detect new columns in CSV files
- Update table schema while preserving existing structure
- Maintain compatibility with downstream ETL jobs
For breaking changes like removed columns, use the “Update the table definition in the Data Catalog” setting. This controls schema overwrites.
Building Basic ETL Jobs
Ready to turn raw data into useful insights? This guide will show you how to make your first AWS Glue ETL jobs. We’ll use the NYC parking tickets dataset to teach you how to extract, transform, and load data. It’s great for those wanting to learn AWS Glue step by step.
Job Creation Wizard Walkthrough
Begin your ETL journey with Glue’s easy-to-use interface. The job wizard makes complex tasks simple by guiding you through each step:
- Pick your data source from the catalog (we’ll use NYC parking violations CSV)
- Choose how you want to transform the data – like filtering out bad license plates
- Decide where to put the processed data in S3
Pro Tip: Use AWS CloudFormation templates to save time. They help you set up jobs quickly and easily across different environments.
Script Editing in Glue Studio
For more control, switch to coding. Here’s how it compares to the visual editor:
| Feature | Visual Editor | Code Editor |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Beginner-friendly | Python/Scala knowledge needed |
| Customization | Basic transformations | Advanced data manipulation |
| Execution Speed | Faster setup | Optimized performance |
Change the auto-generated PySpark scripts to handle unique cases. For example, you can convert violation timestamps to UTC format. The debugger in Glue Studio helps find and fix errors before running the job.
Job Scheduling and Triggers
Make your workflow automatic with flexible scheduling:
- Time-based: Run jobs daily at 2 AM
- Event-driven: Start jobs when S3 buckets update
- Dependent workflows: Link several ETL processes together
Set up error retry policies for issues like network timeouts. Use the console to track job histories and improve performance over time.
Transforming Data with Glue ETL
Data transformation makes raw info ready for analysis. AWS Glue makes this easier with visual tools and code options. Let’s look at ways to efficiently change your data.

Common Transformation Examples
Glue makes simple data cleanup tasks easy. Here are three common examples:
- Date standardization: Change different date formats to ISO 8601
- Currency normalization: Make all money values in one currency, like USD
- Null value handling: Fill in missing data with defaults or calculated values
| Transformation | Input Example | Output | Glue Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Column Renaming | cust_id → customer_id | Consistent naming | ApplyMapping |
| Type Casting | “2025” (string) | 2025 (integer) | ResolveChoice |
| Pattern Matching | Phone: (555) 123-4567 | 5551234567 | RegexReplace |
Using Built-in Transform Functions
Glue Studio has over 40 transforms for common tasks. The ApplyMapping function helps:
- Change column order in output datasets
- Change data types during extraction
- Remove unnecessary fields early
For currency changes, use Spigot and DropNullFields. These tools make coding for simple tasks unnecessary.
Custom Code Implementation
For unique business rules, use Python or Scala. Create UDFs for:
- Special calculations (like in pharma)
- Adjusting data from old systems
- Creating features for machine learning
| Factor | Built-in Functions | Custom Code |
|---|---|---|
| Development Speed | Fast (drag-and-drop) | Slower (coding required) |
| Flexibility | Limited to prebuilt options | Unlimited customization |
| Maintenance | AWS-managed | Team responsibility |
In our aws glue basics tutorial, we mix both ways. Use Map for order totals, then add custom logic for rewards.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
When you start using AWS Glue, it’s key to know how to watch your workflows and fix problems. This part talks about the main tools and ways to keep your ETL jobs going well. It’s all about getting started with AWS Glue.
CloudWatch Metrics Overview
AWS Glue works well with Amazon CloudWatch for tracking performance in real-time. Important metrics like JobRunTime, DPUUsage, and CompletedJobs show how well resources are used. Create custom dashboards to watch:
- Data processing rates
- Error frequencies
- Memory consumption patterns
Job Run History Analysis
The AWS Glue console keeps a detailed log of all job runs. You can filter by date, job status, or error codes to find patterns. This helps you:
- Find recurring performance issues
- Check if transformations worked right
- Save on costs by better using DPU
Common Error Patterns
When getting started with AWS Glue, you might run into these problems:
- S3 Access Denied: Check bucket policies and IAM role permissions
- Job Timeouts: Raise timeout limits or make complex transformations better
- Schema Mismatches: Update crawler settings for new data formats
- Resource Exhaustion: Increase DPU capacity for bigger datasets
- Crawler Stalls: Look at network settings and VPC routing
Most errors show up in CloudWatch logs with specific error codes. Use these to fix problems faster.
Security Best Practices
Keeping your data safe in AWS Glue is key. You need to focus on access controls, data protection, and network security. Here are some steps to keep your data safe while keeping your workflow smooth.
IAM Role Management
Implement least-privilege access for all Glue operations. First, create special IAM roles for tasks like crawlers or jobs. Here’s how:
- Navigate to IAM console > Roles > Create role
- Select “AWS Glue” as trusted entity
- Attach policies that fit your job’s needs
| Role Type | Recommended Policy | Access Level |
|---|---|---|
| Crawler Role | AWSGlueServiceRole | Read-only S3 access |
| ETL Job Role | AmazonS3FullAccess | Specific bucket only |
| DevOps Role | AWSGlueConsoleFullAccess | With MFA requirement |
Data Encryption Methods
AWS Glue has many ways to encrypt data. Use AWS KMS for:
- Catalog metadata encryption
- S3 data encryption using SSE-KMS
- Job bookmark encryption

Always encrypt sensitive data before processing. AWS provides native tools that simplify this process without impacting performance.
VPC Configuration Tips
Use these VPC strategies for secure network communication:
- Create private subnets for Glue connections to databases
- Use security groups to restrict inbound/outbound traffic
- Set up VPC peering for hybrid cloud environments
For on-premises data sources, set up a VPN with:
- IPsec protocol encryption
- Network Address Translation (NAT) gateways
- Regular security group audits
These steps create a strong base for your AWS Glue operations. Always check your settings as your data needs change. Use AWS CloudTrail for ongoing monitoring.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Managing AWS Glue costs involves three main areas: resource use, timing, and service limits. For beginners, finding the right balance between performance and budget can be tough. But, with these strategies, you can stay efficient without spending too much.
DPU Usage Monitoring
Data Processing Units (DPUs) are key for your ETL jobs. Each unit has 4 vCPUs and 16 GB of memory. Keep an eye on DPU use through:
- AWS Glue job metrics in CloudWatch
- Cost Explorer’s hourly/daily reports
- Job blueprint recommendations
Set alerts for when jobs use more than 80% of their DPUs. For small tasks, start with 2 DPUs. Only increase if needed to avoid slowdowns.
Job Scheduling for Cost Efficiency
Using time-based triggers can cut costs by 40-60% compared to on-demand jobs. Here’s a comparison:
| Factor | On-Demand Jobs | Scheduled Jobs |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per DPU-hour | $0.44 | $0.29 |
| Ideal Use Case | Urgent data pipelines | Regular maintenance |
| Savings Possible | Base rate | Up to 34% |
Run non-urgent jobs during off-peak hours (e.g., 8 PM – 4 AM local time) with cron expressions. Also, merge small jobs into one execution when possible.
Free Tier Limitations
AWS Glue’s free tier includes 1 million objects/month catalog storage and 40 DPU-hours. New users often face these issues:
- Unmonitored crawler runs using DPUs
- Storing extra table versions
- Keeping test jobs running
Turn on billing alerts at 80% of free tier limits. Also, delete unused development catalogs every week to avoid storage overages.
Real-World Use Cases
Learning about real-world uses makes AWS Glue more meaningful. Let’s look at three scenarios where AWS Glue excels. These examples show how the AWS Glue tutorial series helps solve real business problems.
Data Lake Management
Netflix uses AWS Glue to manage huge amounts of unstructured data. It automatically makes files in S3 buckets searchable. The benefits include:
- Automated schema discovery for CSV, JSON, and Parquet files
- Cross-account data access through centralized catalog
- Real-time updates when source data changes
A healthcare provider cut data prep time by 70% with Glue crawlers. This matches the AWS Glue tutorial series advice for managing data well.
Database Migration Scenarios
Need to move a 10TB MySQL database to Redshift? AWS Glue makes schema conversion and data transfer easy. A fintech company moved their database in 48 hours with:
| Stage | Glue Feature | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Schema Mapping | Data Catalog | 8 hours |
| Data Transfer | DynamicFrames | 12 hours |
| Validation | Job Metrics | 4 hours |
The migration job used 25 DPUs and incremental loading to reduce downtime. Glue’s error retry feature handled network issues smoothly.
Analytics Pipeline Setup
E-commerce companies use AWS Glue for clickstream analysis. A fashion retailer processes 5 million daily events with this pipeline:
- Raw click data goes to S3 via Kinesis Firehose
- Glue jobs clean and enrich records hourly
- Processed data loads into Athena for SQL queries
Our analytics team reduced report generation time from 6 hours to 20 minutes using Glue’s partitioned datasets.
This setup follows the AWS Glue tutorial series for event-driven architectures. It helps teams understand user behavior while keeping costs low with job bookmarks.
Integrating with Other AWS Services
AWS Glue works best when paired with other AWS tools. This integration helps you create complete data pipelines easily. You don’t have to worry about setting up infrastructure. Let’s look at three key services that boost your ETL workflows.
Athena Query Integration
Combine AWS Glue with Athena for a strong analytics team. Glue’s Data Catalog feeds Athena, making it easy to query data. For instance:
- Run SQL queries on S3 data processed through Glue ETL jobs
- Create virtual tables from Glue catalog entries
- Optimize query speed using partitioned data layouts
Athena’s serverless nature complements Glue perfectly – you pay only for the queries you run on prepared datasets.
Redshift Data Loading
Here’s how to move data to Redshift in three steps:
- Configure Glue connections to your Redshift cluster
- Use glueContext.write_dynamic_frame.from_jdbc_conf in scripts
- Schedule hourly/daily loads using Glue triggers
This setup supports both full loads and incremental updates. It’s perfect for data warehouses.
Lambda Function Triggers
Use this serverless combo for event-driven pipelines:
| Event Source | Lambda Action | Glue Response |
|---|---|---|
| S3 File Upload | Trigger function | Start ETL job |
| CloudWatch Alarm | Send notification | Retry failed jobs |
| API Gateway Call | Validate request | Initiate custom workflow |
This setup is great for real-time data processing. When new files arrive in S3, Lambda starts your Glue jobs automatically. No need for manual steps.
Pro Tip: Use AWS EventBridge for complex trigger patterns. It combines multiple services for workflows like data validation → transformation → archiving in one go.
Advanced Tips for Beginners
After learning the basics of AWS Glue, these pro-level strategies will make you more efficient. We’ll look at three ways to improve your data workflow and reduce mistakes.
Bookmark Management
AWS Glue’s job bookmarks are like progress trackers for your ETL jobs. They help when you’re working with incremental data, like daily sales records. This way, jobs only process new or changed files. Here’s how to turn it on:
- Check “Enable job bookmark” during job creation
- Set partition thresholds to control batch sizes
- Use
job.commit()in scripts to save progress
This can make your jobs up to 40% faster, according to AWS.
Job Retry Strategies
Jobs can fail due to network issues or temporary resource shortages. To handle this, set up automatic retries with:
- Exponential backoff: Start with 1-minute delays, doubling each attempt
- Max retries set to 3-5 (balance cost vs reliability)
- Error pattern matching to skip unfixable failures
Pair this with CloudWatch alerts to keep your pipeline running smoothly without constant checks.
Version Control Basics
Manage your ETL scripts like you would production code. For beginners, start with:
- Git repositories for script storage
- Branching strategies for testing transformations
- Commit messages tracking business logic changes
Keep connection strings and credentials outside version control using AWS Secrets Manager for security.
Building Your AWS Glue Expertise Path
This AWS Glue tutorial for beginners has given you key skills for serverless ETL operations. You’ve learned to set up crawlers, create data catalogs, and run transformation jobs. These basics are a solid start for tackling today’s data integration tasks in S3, Redshift, and other cloud storage.
To get better, think about getting AWS certifications like the AWS Certified Data Analytics – Specialty. Doing projects like moving on-premise databases to cloud data lakes or making analytics pipelines for IoT devices will help. Check out AWS’s official documentation and GitHub for examples on real-world tasks like managing retail inventory or processing healthcare data.
Use AWS’s built-in metrics and CloudWatch to track your progress. Begin with weekly crawler schedules and simple JOIN transformations. Then, move on to more complex workflows with Lambda triggers and Glue Elastic Views. Don’t forget to use cost-control tools like DPU monitoring and job bookmarks.
Keep up with AWS re:Invent announcements and the AWS Big Data Blog. Combine your Glue skills with services like Athena for better queries and Lake Formation for security. Regular practice with different datasets will turn these skills into real-world abilities.
FAQ
How does AWS Glue differ from traditional ETL tools?
AWS Glue is different because it doesn’t need you to manage servers. It’s fully managed and serverless. Traditional ETL tools need you to set up servers and define schemas yourself. Glue uses Data Processing Units (DPUs) to scale automatically and works well with AWS services like S3 and Redshift. Glue Crawlers also automatically find data formats and update the Data Catalog.
What IAM permissions are essential for AWS Glue beginners?
Beginners need AWSGlueServiceRole for jobs, AmazonS3FullAccess for buckets, and CloudWatchLogsFullAccess for monitoring. It’s important to follow the least-privilege principle. For example, limit S3 access to specific buckets. Businesses should use AWS Organizational SCPs to set rules for teams.
How do AWS Glue Crawlers handle schema changes automatically?
Crawlers keep track of schema changes through schema versioning in the Data Catalog. For example, if a Shopify feed adds new columns, crawlers will mark them as Schema Change: Add Column. You can set up crawlers to update table definitions while keeping them compatible with older versions.
How can I avoid unexpected costs in AWS Glue?
Keep an eye on DPU hours with AWS Cost Explorer and set up billing alarms. Use job bookmarks for incremental processing to avoid scanning all data. Run non-urgent jobs when it’s less busy. Also, test transformations locally with Glue Development Endpoints before running them in the cloud to save on trial costs.
What are common errors when creating first AWS Glue jobs?
Common problems include S3 Access Denied errors (fix with bucket policies), DPU capacity limits (ask for more quota), and timeout errors (adjust job timeouts). Always check CloudWatch Logs for specific error codes. For example, ResourceNotReadyException often means IAM role issues.
How does AWS Glue integrate with Athena and Redshift?
Glue Data Catalog is the central metadata repository for both Athena and Redshift. Athena uses Glue table definitions to query Parquet/JSON files in S3. Redshift Spectrum extends SQL queries to S3 data lakes. Use Glue ETL jobs to transform data into formats like Apache Parquet for Redshift.
Can AWS Glue process incremental data loads efficiently?
Yes, use job bookmarks to track processed data. For example, when adding daily CSV files from an SFTP server, bookmarks prevent reprocessing old data. Use S3 event notifications to start Glue jobs only when new data arrives.
What security best practices should I implement with AWS Glue?
Always encrypt Data Catalog metadata with AWS KMS and enable SSL for JDBC connections. For sensitive data, use VPC endpoints to keep Glue traffic private. Regularly audit IAM roles with AWS Config to ensure least-privilege access.
How complex are data transformations in AWS Glue?
Glue has built-in transforms like Filter, Join, and Map for common tasks. For more complex tasks, write custom PySpark code. The visual editor makes simple workflows easy, while code-based jobs offer full customization.
What real-world use cases demonstrate AWS Glue’s value?
AWS Glue is useful for many things like migrating 10TB+ SQL Server databases to S3 data lakes. It’s also great for building clickstream analytics pipelines and automating GDPR compliance workflows. One company migrated to the cloud 70% faster using Glue’s parallel processing.