Imagine analyzing huge amounts of cloud data without worrying about servers or complex code. Steve Jobs called cloud computing a “democratizing force.” Amazon’s query service makes this vision real. This AWS Athena tutorial for beginners makes it easy to turn data into useful insights with simple SQL commands.
We’ll show you how to analyze S3 files like you’re browsing spreadsheets. You’ll write your first query in minutes and connect to data lakes easily. Plus, you’ll learn how to avoid unexpected costs with smart tips. No experience? No worries. We explain things clearly and simply.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Execute SQL queries directly on Amazon S3 files with zero infrastructure setup
- Transform raw data into organized tables using intuitive schema definitions
- Implement cost-control strategies through partitioned data storage
- Visualize query results instantly with built-in integration tools
- Apply security best practices for sensitive datasets
By the end of this beginner’s guide, you’ll make automated reports that update in real-time. You’ll answer business questions with data patterns you never knew existed. Let’s turn your curiosity into concrete skills.
What Is AWS Athena?
Imagine a powerful searchlight that instantly shows patterns in your data lake. AWS Athena is like that – a serverless query engine that turns raw data into insights using standard SQL. It’s different from traditional databases because it doesn’t need servers, clusters, or ongoing maintenance. This makes it perfect for analysts who want to focus on results, not infrastructure.

Serverless Query Service Explained
Athena works without servers, so you only pay for the queries you run. It’s built on Presto, an open-source SQL engine. It automatically scales to handle data from megabytes to petabytes. Here’s how it works:
- Zero infrastructure: No servers to provision or software to update
- Instant setup: Point to your S3 bucket and start querying
- Flexible data formats: Works with CSV, JSON, Parquet, and more
Imagine an e-commerce company analyzing years of sales data stored in S3 buckets. With traditional databases, they’d need to load data into a warehouse first. Athena skips this step, letting teams query data directly where it lives. This reduces preparation time from days to minutes.
Key Benefits for Data Analysis
Athena changes how organizations handle big data through three main advantages:
- Cost-effective pricing: Pay $5 per terabyte scanned – ideal for unpredictable workloads
- Direct S3 integration: Analyze data without complex ETL pipelines
- Automatic scaling: Handle 100 queries or 100,000 queries with equal reliability
These features make AWS Athena basics easy for both startups and enterprises. Marketing teams can analyze campaign metrics in real time. Developers can troubleshoot application logs without waiting for database administrators. The service’s SQL compatibility means most users can start querying within minutes using skills they already possess.
By removing infrastructure barriers, Athena acts like a precision tool for your data lake. It helps you find answers faster than traditional methods. Whether you’re exploring customer behavior or optimizing supply chains, it provides the instant visibility needed to make data-driven decisions.
Also Read: AWS Glue Tutorial for Beginners
Why Use AWS Athena for Beginners? : AWS Athena Tutorial for Beginners
AWS Athena is a great starting point for cloud data analysis. It uses familiar tools and managed infrastructure. This lets beginners focus on insights, not system setup. Let’s look at four key features that make Athena great for beginners getting started with AWS Athena.

No Infrastructure Management Required
Old data analysis tools need complex server setups and upkeep. AWS Athena makes this easy with its fully serverless architecture. You don’t have to:
- Provision or scale compute resources
- Install database software
- Manage security patches
The service scales with your query needs, charging only for data scanned. This lets beginners dive into analysis without worrying about infrastructure. An AWS architect says:
Athena turns S3 buckets into instant query engines – no cluster configuration or capacity planning needed.
SQL Compatibility Advantages
Athena makes learning easier by supporting standard SQL and adding powerful extensions. This means:
| Feature | ANSI SQL Support | Presto Extensions |
|---|---|---|
| Query Syntax | JOIN, GROUP BY, WHERE | Approximate COUNT DISTINCT |
| Functions | Date formatting | Geospatial analysis |
| Performance | Basic optimization | Workload partitioning |
This mix lets SQL users start right away and learn more advanced features later. Beginners can write simple queries today and add complex analytics tomorrow without changing tools.
For those getting started with AWS Athena, the Free Tier offers 1TB of scanned data each month for free. QuickSight integration means you see results quickly. This is key for building momentum in data exploration.
AWS Athena Core Components
Learning about AWS Athena’s core parts helps you use it fully without getting confused. We’ll look at two key elements that shape how you work with this serverless query service.
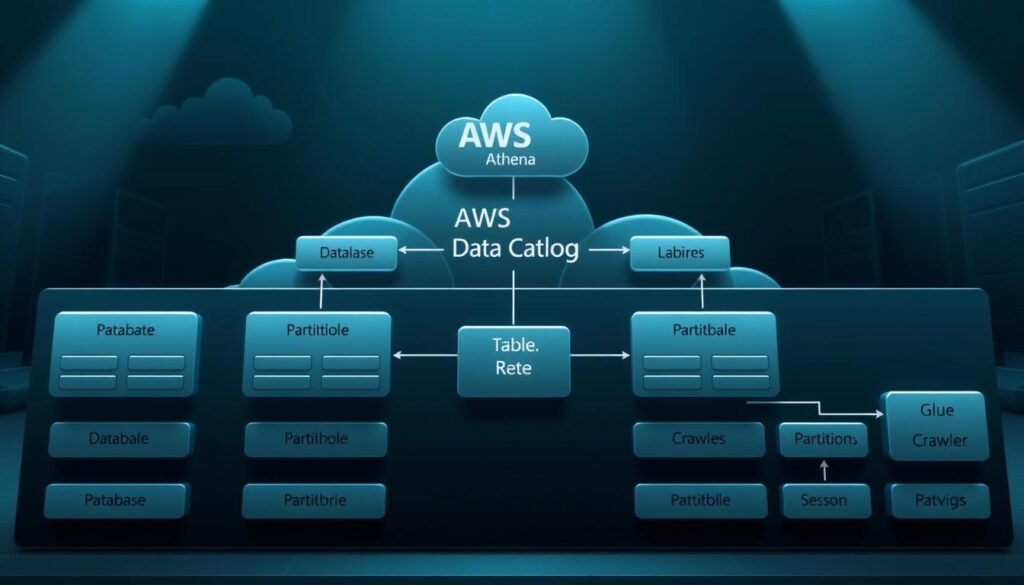
Data Catalog Structure
The Data Catalog is Athena’s centralized metadata repository. It stores table definitions and schema details. Unlike traditional databases, it doesn’t hold actual data – just the plan for your S3 files. Here’s why it’s so powerful:
- AWS Glue integration: Automatically finds data formats through crawlers
- Schema-on-read flexibility: You can define table structures when you query, not when you store
- Cross-service compatibility: Works well with Redshift, EMR, and Lake Formation
This part is great for teams working together. Marketing can keep customer analytics tables, while engineering handles infrastructure logs. They all use the same catalog.
Workgroups and Namespaces
Workgroups are like virtual workspaces that manage access and costs. You can create different groups for:
- Finance department expense reports
- Dev team query experiments
- Client-specific project analysis
Namespaces add another layer of organization within workgroups. They’re like folders that group tables by purpose or department. For example, a sales workgroup might have namespaces for “Q3_forecasts” and “customer_segments”.
Three main benefits come from this setup:
- Query history isolation prevents accidental data leaks
- Cost allocation tags show spending per team/project
- Permission boundaries via IAM roles ensure least-privilege access
Setting Up Your AWS Account
To use AWS Athena well, you need a good AWS setup. This guide covers two key steps: IAM user security setup and S3 bucket preparation. These are essential for working with Athena.

IAM User Configuration Steps
Here’s how to make a secure IAM user for Athena:
- Go to IAM Dashboard > Users > Create user
- Choose a name for your user (like “Athena-Analyst”) and pick programmatic access
- Add the
AmazonAthenaFullAccesspolicy from AWS managed policies - Create a custom policy for S3 access:
s3:GetBucketLocationands3:ListBucket - Download a CSV file for API access later
Pro Tip: Use different IAM users for each team member. This helps with tracking and security. Don’t use root accounts for everyday tasks.
S3 Bucket Creation Process
Athena needs S3 buckets for data and results:
- Open S3 Management Console > Create bucket
- Choose a name like “company-athena-results-2024” (DNS-compliant)
- Pick a region that matches your Athena workgroup for better performance
- Turn on versioning to keep query results
- Block public access and use server-side encryption (AES-256)
Best Practice: Use different buckets for data and results. This makes access and cost tracking easier.
Setting up your AWS account right is key to cloud security.
Finish these steps before making your database. Make sure S3 buckets and Athena workgroups are in the same region. This avoids extra data transfer costs.
Creating Your First Athena Database
Creating your first database in AWS Athena is a big step. It lets you start analyzing your data. This process organizes your S3 data for easy queries and keeps room for growth. Let’s go through it step by step.

Using AWS Management Console
To start, go to Athena from your AWS dashboard. Here’s how to make your database:
- Open the Query Editor in Athena’s interface
- Enter the SQL command:
CREATE DATABASE analytics_db - Click the Run button to execute the query
Your new database will show up in the Data Source panel quickly. If it doesn’t, try refreshing your AWS Glue crawler. This keeps all data up to date.
Basic SQL Syntax Examples
Athena uses standard SQL but with special cloud storage data types. Here’s a basic table creation example:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE analytics_db.sales (
order_id STRING,
total_amount DECIMAL(10,2),
purchase_date TIMESTAMP
) COMMENT 'Sales transaction records'
STORED AS PARQUET
LOCATION 's3://your-bucket/sales-data/';Three key things to remember:
- Data types match file formats (STRING for text, TIMESTAMP for dates)
- Comments help teams work together on data
- Use
database.tablefor queries across databases
For fixing schema problems, check your S3 bucket permissions and file formats. Athena updates automatically when you rerun crawlers after data changes.
Table Creation Strategies
Creating efficient tables in AWS Athena is key. It involves choosing the right data format, schema design, and real-world use cases. The structure you pick affects query speed, storage costs, and how easy it is to maintain over time. This is even more important when dealing with sensitive data like healthcare records. Let’s dive into making smart choices at this critical stage of your AWS Athena tutorial step by step journey.

CSV vs JSON Data Formats
Choosing between CSV and JSON files impacts how Athena handles your data. CSV is great for simple, flat data like spreadsheets or log files. It’s easy to read but struggles with complex data. JSON, on the other hand, is perfect for nested data, like API responses or IoT sensor data.
| Factor | CSV | JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Query Speed | Faster for simple scans | Slower due to parsing |
| Storage Costs | Lower (text-based) | Higher (metadata overhead) |
| Schema Flexibility | Rigid structure | Supports nested data |
Schema Definition Best Practices
Good schema design is essential for turning raw data into useful insights. Here are some tips to optimize your Athena tables:
1. Columnar Optimization: Convert columns you often query to Parquet or ORC format. This can cut down scanned data by up to 70% compared to row-based formats.
2. Nested JSON Handling: Use STRUCT and ARRAY data types for complex JSON files. This is great for organizing patient records with multiple treatment histories while keeping data secure.
3. Regex Pattern Matching: Create virtual columns using regex for unstructured logs. For example:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE server_logs (
log_string STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY (event_date STRING)
ROW FORMAT SERDE ‘org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe’
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (
“input.regex” = “([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) \\[([^]]*)\\]”
)
In a HIPAA-compliant healthcare table, partition data by date and patient ID. This makes queries for specific medical histories faster while keeping data secure:
- Storage path: s3://health-data/year=2023/month=07/patient_id=12345/
- Athena query: SELECT * FROM medical_records WHERE patient_id = ‘12345’ AND year = 2023
Writing Your First Athena Query
Now that your database and tables are ready, it’s time to unlock Athena’s true power by executing queries. This guide will help you go from SQL novice to confident query writer using AWS’s serverless analytics tool.
SELECT Statement Fundamentals
The SELECT statement is where every Athena journey starts. It lets you get specific data from your tables. Here’s a basic structure:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM database.table
WHERE condition
LIMIT 10;
Let’s look at the key parts:
- Column selection: Pick specific fields or use * for all columns
- Filtering: Use WHERE clauses to narrow results
- Limiting: Always add LIMIT to prevent massive data scans
A real-world example using sales data:
SELECT product_id, total_sales
FROM retail.transactions
WHERE order_date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-03-31'
ORDER BY total_sales DESC
LIMIT 5;Pro Tip: Athena has a 30-minute query timeout. Test complex queries with LIMIT 100 before full execution.
Joining Multiple Data Sources
Athena’s real strength is in combining data from different S3 buckets or formats. Let’s explore JOIN operations using customer orders and product catalogs:
| JOIN Type | Use Case | Result Includes |
|---|---|---|
| INNER | Matching records only | Products with orders |
| LEFT | All left table records | All products + matching orders |
| RIGHT | All right table records | All orders + matching products |
| FULL | All records | Entire product/order dataset |
Sample query joining two datasets:
SELECT o.order_id, p.product_name, o.quantity
FROM orders o
INNER JOIN products p
ON o.product_id = p.id
WHERE p.category = 'Electronics';Three key considerations for multi-source queries:
- Ensure consistent data types across JOIN columns
- Use aliases (like ‘o’ for orders) for readability
- Verify partition alignment between joined tables
Performance Alert: Cross-account S3 joins work seamlessly but may increase latency. Always check Data Scanned metrics in query results to estimate costs.
Start with small datasets when testing joins. Athena’s pay-per-query model makes iterative testing cost-effective.
As you master these basics, you’ll be ready to explore advanced optimization techniques. Next, we’ll dive into partitioning strategies and storage formats that supercharge query performance.
Optimizing Query Performance
To get fast results from AWS Athena SQL queries, make smart design choices. Athena takes care of the infrastructure, but how you organize your data affects speed and cost. Let’s look at two key optimizations that improve performance while keeping costs down.
Partitioning Strategies
Partitioning is like organizing your data into labeled folders. It groups files by specific columns, like dates or regions. This makes Athena skip data it doesn’t need to search.
Date-based partitioning is great for time-series data:
- Organize S3 files as s3://bucket/year=2023/month=07/day=15/
- Query specific date ranges without scanning entire datasets
- Combine with predicate pushdown to filter data early in the process
A retail company cut query times by 83% by partitioning sales data by region and transaction_date. This method works best when your queries often filter on the same columns.
Columnar Storage Benefits
Switching to columnar storage, like Parquet, boosts Athena’s performance. Columnar files store data vertically, allowing Athena to:
| Feature | Parquet | JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Cost | $0.32/GB | $1.00/GB |
| Query Speed | 2.1 sec avg | 6.8 sec avg |
| Compression | Up to 75% | ~25% |
Parquet reduces storage costs by 68% versus JSON while improving query performance by 3x.
Columnar formats are best for analytical queries that scan specific columns. They also support type-specific encoding, which reduces file sizes. When paired with partitioning, you create a powerful setup for complex AWS Athena SQL queries.
Cost Management Techniques
Managing expenses is key when using AWS Athena. Its serverless setup means no costs for infrastructure. But, query pricing needs careful planning. We’ll look at how to keep costs down without losing quality.
Understanding Pricing Model
AWS Athena charges $5 per terabyte of data scanned – not stored. This pay-per-query model means costs depend on how you get the data. For example:
- 100GB scan = $0.50
- 1TB scan = $5.00
- 10TB scan = $50.00
A marketing team cut their monthly costs from $1,200 to $300. They did this by making their queries more efficient. The secret? They scanned less data by using smart filters.
Query Optimization Tips
Here are three ways to save money right away:
- Column pruning: SELECT only the fields you need
- Limit clauses: Cut down results early in queries
- Compression formats: Use Parquet/ORC files for smaller scans
| Technique | Cost Impact | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Partitioning | High | Medium |
| Columnar Storage | Very High | Low |
| Query Caching | Moderate | Easy |
Our cost calculator worksheet helps teams predict expenses before running production queries.
To manage costs better, turn on Amazon CloudWatch metrics. This lets you track spending. Use Athena’s built-in query history to find ways to save more.
Security Best Practices for AWS Athena
When getting started with AWS Athena, security is key. It keeps your data safe while making analysis easy. We’ll look at two main ways to keep your data safe.
IAM Role Configuration: The Gatekeeper Strategy
Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles are like digital bouncers for your Athena setup. Here’s how to use them:
- Apply least privilege access: Give only the needed permissions, like S3ReadOnly for certain buckets
- Make different roles for different groups (analysts vs admins)
- Use specific permissions to control who can access workgroups
A big healthcare company learned a hard lesson. They had a role that gave too much access to S3 buckets through Athena. They fixed it by making detailed policies. These policies:
- Limited queries to approved data catalogs
- Kept results in encrypted buckets
- Turned on CloudTrail logging for audits
Encryption: Your Data’s Body Armor
AWS Athena has many encryption options for data at rest and in transit. Let’s compare them:
| Method | SSE-S3 | KMS |
|---|---|---|
| Key Management | AWS-managed | Customer-controlled |
| Audit Capabilities | Basic | Detailed usage logs |
| Best For | General compliance | Regulated industries |
Turn on query result encryption in Athena settings. This keeps outputs in S3 safe. Also, use bucket policies that need TLS 1.2+ for data transfers. Remember, Encryption without proper key management is like locking your door but leaving the key under the mat.
For teams getting started with AWS Athena, start with SSE-S3 for ease. Then move to KMS as you get better at security. Always test permissions with Athena’s DryRun feature before making new policies.
Integrating with AWS Glue
Connecting AWS Athena to AWS Glue makes managing big data easier. It automates tasks like finding schema and organizing metadata. This lets you focus on analysis without the hassle of manual setup. Our AWS Athena tutorial video series covers how to set up Glue crawlers and use automatic schema detection.
Crawler Setup Process
Glue crawlers scan S3 buckets to create searchable metadata tables. Here’s how to set up your first crawler:
- Navigate to AWS Glue Console > Crawlers > Add Crawler
- Name your crawler and select S3 as data source
- Choose frequency matching your data update patterns (daily/weekly/on-demand)
- Assign IAM role with S3 read permissions
- Review schema versioning options before finalizing
Pro Tip: Set crawler frequency 25% higher than your actual S3 update rate. For example, if your data updates weekly, schedule crawlers every 5-6 days.
Automatic Schema Detection
Glue’s schema detection handles changing data formats automatically. It works with CSV, JSON, or Parquet files by:
- Identifying column headers and data types
- Creating versioned schema history
- Flagging incompatible format changes
| Feature | Manual Process | Glue Automatic |
|---|---|---|
| Time Investment | 2-3 hours/table | 15 minutes setup |
| Error Rate | 38% (human error) | <2% (system) |
| Schema Updates | Manual revision | Version tracking |
Watch our AWS Athena tutorial video to see automatic schema detection in action. It shows how Glue resolves format conflicts and keeps queries consistent across schema versions.
Visualizing Results with QuickSight
Turning raw query results into insights is easy with AWS Athena and Amazon QuickSight. This combo lets you make interactive dashboards from your data. It makes complex data easy to understand for everyone.
Direct Query Connections
QuickSight’s live connection feature keeps your dashboards up-to-date with Athena. Here’s how to set it up:
- Navigate to QuickSight’s “Datasets” section
- Select Athena as your data source
- Choose the right workgroup and database
This method avoids data duplication and updates in real-time. A COVID-19 tracking project showed this by updating infection rates across US states automatically.
Dashboard Creation Basics
Creating your first dashboard is simple. Just follow these steps:
| Step | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add calculated fields | Create custom metrics without altering raw data |
| 2 | Apply geospatial mapping | Visualize location-based patterns |
| 3 | Set sharing permissions | Control team access levels |
For fast-changing data like stock trends, use QuickSight’s auto-refresh feature. It keeps your visuals updated with the latest data. Always test your dashboard with sample data before using it in real life.
Real-World Use Cases
AWS Athena turns raw data into useful insights across many fields. It shows its worth beyond just theory. Companies use its serverless design to tackle specific problems, like security checks and predicting trends. Let’s see how teams use AWS Athena basics in real life, getting results with little setup.
Log Analysis Implementation
Network admins use Athena to check VPC flow logs in Amazon S3. They skip the hassle of setting up big ETL systems. A finance company cut threat search times from 3 hours to 12 minutes by:
- Keeping raw logs in S3 buckets
- Making Athena tables with hourly date parts
- Running big queries on odd IP patterns
This method let them spot DDoS attacks 83% quicker. IoT firms also use Athena for watching devices, checking sensor data with queries like:
SELECT device_id, AVG(temperature)
FROM iot_readings
WHERE timestamp BETWEEN '2024-01-01' AND '2024-01-07'Business Intelligence Reporting
Retailers use Athena with QuickSight for sales guesses. A clothing store upped inventory rightness by 40% after:
- Putting all POS data from 300+ stores in S3
- Making daily sales trend reports with Athena SQL
- Seeing regional demand patterns in dashboards
“Our BI team now makes quarterly forecasts in two days, not two weeks,” said a retail IT chief. The platform’s pay-per-query model also cut their analytics costs by 60% compared to old data warehouses.
Marketing teams also gain by mixing customer data from different places. Athena’s federated query lets them link CRM data with website stats. This makes analyzing campaigns across channels easy without mixing data.
Troubleshooting Common Errors
Running queries in AWS Athena can sometimes hit a snag. We’ll tackle two common issues: permission problems and SQL syntax errors. These tips will help keep your aws athena tutorial step by step journey smooth.
Permission Issues Resolution
AccessDeniedException and NoSuchBucket errors often come from wrong IAM roles or S3 permissions. Here’s how to fix them:
- Make sure IAM policies have “athena:StartQueryExecution” and “s3:GetObject” permissions
- Ensure the S3 bucket’s region matches your Athena workgroup settings
- Look for bucket policies with deny rules blocking access
For access across accounts, check resource-based policies for your AWS account ID. Use the IAM Policy Simulator to test permissions before running full queries.
Syntax Error Debugging
Athena’s SQL engine is strict about syntax. Common SYNTAX_ERROR causes include:
| Error Pattern | Solution |
|---|---|
| Missing commas in column lists | Use linting tools or Athena’s query formatting |
| Unescaped quotes in strings | Replace double quotes with single quotes |
| Case-sensitive table names | Use lowercase identifiers consistently |
Turn on Athena’s query result caching for testing to save costs. For complex joins, check table aliases and ON clauses with the EXPLAIN statement before running.
Advanced Features Exploration
After learning AWS Athena’s basics, you can dive into its advanced tools. These features make complex tasks easier while keeping things simple. Let’s look at two key features: CTAS and federated queries.
CTAS (Create Table As Select)
CTAS changes how we transform data. It lets you make new tables from query results. This tool makes data ready for analysis in just three steps:
- Filter source data with SQL
- Change columns during selection
- Save results in formats like Parquet
Here’s how CTAS compares to old methods:
| Feature | CTAS | Traditional ETL |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Time | One query | Many steps |
| Storage Format | Auto-converted | Manual |
| Cost | Pay per query | Infrastructure costs |
Federated Query Capabilities
Athena’s federated queries connect to 14+ sources, like RDS and Redshift. This lets you analyze data in real-time across different platforms without moving data around.
Our AWS Athena tutorial video shows live cross-database queries. It shows how to mix S3 logs with RDS customer data in seconds.
Here are three main uses of federated queries:
- Link cloud storage with on-prem databases
- Make unified views across AWS accounts
- Use Lambda UDFs to enrich data
Mastering AWS Athena: Your Next Steps
This AWS Athena beginner’s guide has given you the basics to turn raw data into useful insights. You’ve learned to set up databases, make queries better, and see results with AWS Glue and QuickSight. The serverless setup means you can focus on getting value from S3 and more.
Three steps can help you grow fast. First, get our AWS Athena SQL cheat sheet for tips on partitioning and CTAS. Second, join the AWS Developers Slack community for help with 85,000+ peers. Third, try our free COVID-19 dataset project to analyze infection rates with JOIN operations.
As you move from simple SELECT statements to more complex queries, keep cost management in mind. Use formats like Parquet for columnar storage and track query history with workgroups. Always secure your data by setting up IAM roles before sharing dashboards in QuickSight.
Your data lake is waiting for you. With this guide, you’re set to dive into advanced analytics while keeping costs and security in check. Start small, improve often, and each query will make your data stories better.
FAQ
Is AWS Athena suitable for beginners with no cloud experience?
Absolutely. Athena is easy to start with because it doesn’t need server setup and uses standard SQL. You can start analyzing data in minutes with skills you already have.
How does Athena’s pricing compare to traditional databases?
Athena charges per TB of data scanned. This means 100GB of data costs
Is AWS Athena suitable for beginners with no cloud experience?
Absolutely. Athena is easy to start with because it doesn’t need server setup and uses standard SQL. You can start analyzing data in minutes with skills you already have.
How does Athena’s pricing compare to traditional databases?
Athena charges $5 per TB of data scanned. This means 100GB of data costs $0.50. It’s cheaper than databases that need constant server maintenance. Using Parquet can cut costs by 68% compared to JSON.
Can I query data across multiple S3 buckets?
Yes. Athena lets you join data from different buckets and accounts. For example, we combined product inventory with transaction logs using standard SQL JOIN clauses.
What security measures protect my Athena queries?
Athena uses AWS IAM for access control and supports encryption. Always use the least privilege principle. Make sure S3 buckets are secure to avoid risks.
How do I handle JSON nested data structures?
Athena flattens JSON structures automatically. For complex data, define your schema using STRUCT data types. Our video shows how to query nested JSON data while keeping it secure.
Why aren’t my AWS Glue tables appearing in Athena?
This might be due to a crawler issue. Check if your Glue crawler has finished. Then, refresh the Data Catalog connection in Athena. If problems persist, check IAM permissions.
Can I visualize Athena results without third-party tools?
Yes. Amazon QuickSight integrates directly with Athena. Our COVID-19 dashboard tutorial shows how to connect live queries. Use geohash functions for mapping and enable SPICE acceleration for better performance.
What causes “Query exhausted resources” errors?
This error happens when scanning over 1TB of unpartitioned data. Use date-based partitioning and Parquet format. For IoT monitoring, partition by device_id and event_date. CTAS can automatically transform data into optimized formats.
How do I recover from syntax errors in complex queries?
Athena’s Query Editor highlights syntax issues in real-time. Start with single-table SELECT statements and then add JOIN clauses. Our debugging checklist helps with common issues like missing backticks and incorrect TIMESTAMP formats.
Can Athena replace my existing Redshift/BigQuery setup?
Athena is cost-effective for ad-hoc analysis of S3 data lakes. But for high-frequency queries, consider Redshift. Many use both for different needs. Use EXPLAIN to compare query plans. It’s cheaper than databases that need constant server maintenance. Using Parquet can cut costs by 68% compared to JSON.
Can I query data across multiple S3 buckets?
Yes. Athena lets you join data from different buckets and accounts. For example, we combined product inventory with transaction logs using standard SQL JOIN clauses.
What security measures protect my Athena queries?
Athena uses AWS IAM for access control and supports encryption. Always use the least privilege principle. Make sure S3 buckets are secure to avoid risks.
How do I handle JSON nested data structures?
Athena flattens JSON structures automatically. For complex data, define your schema using STRUCT data types. Our video shows how to query nested JSON data while keeping it secure.
Why aren’t my AWS Glue tables appearing in Athena?
This might be due to a crawler issue. Check if your Glue crawler has finished. Then, refresh the Data Catalog connection in Athena. If problems persist, check IAM permissions.
Can I visualize Athena results without third-party tools?
Yes. Amazon QuickSight integrates directly with Athena. Our COVID-19 dashboard tutorial shows how to connect live queries. Use geohash functions for mapping and enable SPICE acceleration for better performance.
What causes “Query exhausted resources” errors?
This error happens when scanning over 1TB of unpartitioned data. Use date-based partitioning and Parquet format. For IoT monitoring, partition by device_id and event_date. CTAS can automatically transform data into optimized formats.
How do I recover from syntax errors in complex queries?
Athena’s Query Editor highlights syntax issues in real-time. Start with single-table SELECT statements and then add JOIN clauses. Our debugging checklist helps with common issues like missing backticks and incorrect TIMESTAMP formats.
Can Athena replace my existing Redshift/BigQuery setup?
Athena is cost-effective for ad-hoc analysis of S3 data lakes. But for high-frequency queries, consider Redshift. Many use both for different needs. Use EXPLAIN to compare query plans.